![]() NEET 2015
NEET 2015
|
Section |
Questions |
Marks |
|
Physics |
45 Questions (1 – 45) |
180 |
|
Chemistry |
45 Questions (46 – 90) |
180 |
|
Biology |
90 Questions (91 – 180) |
360 |
![]() Q. 1 If force (F ), velocity (V) and time (T) are chosen as fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
Q. 1 If force (F ), velocity (V) and time (T) are chosen as fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be
A. [E V^(−2) T^(−1)]
B. [E V^(−1) T^(−2)]
C. [E V^(−2) T^(−2)]
D. [E^(-2) V^(−1) T^(−3)]
![]() Q. 2 A Ship A is moving westwards with a speed of 10 km h⁻¹ and a ship B 100 km south of A is moving northwards with a speed of 10 km h⁻¹. The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest is
Q. 2 A Ship A is moving westwards with a speed of 10 km h⁻¹ and a ship B 100 km south of A is moving northwards with a speed of 10 km h⁻¹. The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest is
A. 0 h
B. 5 h
C. 5√2 h
D. 10√2 h
![]() Q. 3 A particle of unit mass undergoes one-dimensional motion such that its velocity varies according to υ(x)=βx-2n where β and n are constants and x is the position of the particle. The acceleration of the particle as a function of x is given by
Q. 3 A particle of unit mass undergoes one-dimensional motion such that its velocity varies according to υ(x)=βx-2n where β and n are constants and x is the position of the particle. The acceleration of the particle as a function of x is given by
A. -2 n β^2 x^(-2n-1)
B. -2 n β^2 x^(-4n-1)
C. -2 n β^2 x^(-2n+1)
D. -2 n β^2 x^(-4n+1)
![]() Q. 4 Three blocks A, B and C, of masses 4 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg, respectively, are in contact on a frictionless surface, as shown. If a force of 14 N is applied on the 4 kg block, then the contact force between A and B is
Q. 4 Three blocks A, B and C, of masses 4 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg, respectively, are in contact on a frictionless surface, as shown. If a force of 14 N is applied on the 4 kg block, then the contact force between A and B is
A. 2 N
B. 6 N
C. 8 N
D. 18 N
![]() Q. 5 A block A of mass m1 rests on a horizontal table. A light string connected to it passes over a frictionless pulley at the edge of table and from its other end another block B of mass m2 is suspended. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is μk. When the block is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
Q. 5 A block A of mass m1 rests on a horizontal table. A light string connected to it passes over a frictionless pulley at the edge of table and from its other end another block B of mass m2 is suspended. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is μk. When the block is sliding on the table, the tension in the string is
A. (m2 +μk m1 )g / (m1 + m2)
B. (m2 -μk m1 )g / (m1 + m2)
C. (m2 . m2(μk + 1))g / (m1 + m2)
D. (m2 . m2(1 – μk))g / (m1 + m2)
![]() Q. 6 Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ. They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then y the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as in case (a) and case (b), respectively:
Q. 6 Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ. They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then y the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as in case (a) and case (b), respectively:
A. WP = WQ; WP > WQ
B. WP = WQ; WP = WQ
C. WP > WQ; WQ > WP
D. WP < WQ; WQ < WP
![]() Q. 7 A block of mass 10 kg, moving in the x-direction with a constant speed of 10 ms⁻¹ subjected to a retarding force F = 0.1x J/m during its travel from x = 20 m to 30 m. final KE will be
Q. 7 A block of mass 10 kg, moving in the x-direction with a constant speed of 10 ms⁻¹ subjected to a retarding force F = 0.1x J/m during its travel from x = 20 m to 30 m. final KE will be
A. 475 J
B. 450 J
C. 275 J
D. 250 J
![]() Q. 8 A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power k watts. If the particle starts from rest the force on the particle at time t is
Q. 8 A particle of mass m is driven by a machine that delivers a constant power k watts. If the particle starts from rest the force on the particle at time t is
A. (√mk / 2) t⁻¹/²
B. (√mk ) t⁻¹/²
C. (√2mk ) t⁻¹/²
D. 1 / (√mk ) t⁻¹/²
![]() Q. 9 Two particles of masses m1, m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2. On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energyε . If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2 then we must have
Q. 9 Two particles of masses m1, m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2. On collision, one of the particles get excited to higher level, after absorbing energyε . If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2 then we must have
A. m1^(2) u1 +m2^(2) u2 -ε = m1^(2) v1 +m2^(2) v2
B. 1/2 (m1^(2) u1 +m2^(2) u2 ) = 1/2 (m1^(2) v1 +m2^(2) v2) – ε
C. 1/2 (m1 u1^(2) +m2 u2^(2) ) – ε = 1/2 (m1^ v1^(2) +m2 v2^(2))
D. 1/2 (m1^(2) u1 +m2^(2) u2 ) – ε = 1/2 (m1^(2) v1 +m2^(2) v2)
![]() Q. 10 The rod of weight W is supported by two parallel knife edges A and B and is in equilibrium in a horizontal position. The knives are at a distance d from each other. The centre of mass of the rod is at distance x from A. The normal reaction on A is
Q. 10 The rod of weight W is supported by two parallel knife edges A and B and is in equilibrium in a horizontal position. The knives are at a distance d from each other. The centre of mass of the rod is at distance x from A. The normal reaction on A is
A. Wx / d
B. Wd / x
C. W(d – x) / x
D. W(d – x) / d
![]() Q. 11 A mass m moves in a circle on a smooth horizontal plane with velocity v0 at a radius R0. The mass is attached to a string which passes through a smooth hole in the plane as shown. The tension in the string is increased gradually and finally m moves in a circle of radius R0. The final value of the kinetic energy is
Q. 11 A mass m moves in a circle on a smooth horizontal plane with velocity v0 at a radius R0. The mass is attached to a string which passes through a smooth hole in the plane as shown. The tension in the string is increased gradually and finally m moves in a circle of radius R0. The final value of the kinetic energy is
A. m v^2 R0
B. 1/4 m v^2 R0
C. 2 m v^2 R0
D. 1/2 m v^2 R0
![]() Q. 12 Three identical spherical shells, each of mass m and radius r placed as shown in figure. Consider an axis XX’ which is touching to two shells and passing through diameter of third shell. Moment of inertia of the system consisting of these three spherical shells about XX’ axis is
Q. 12 Three identical spherical shells, each of mass m and radius r placed as shown in figure. Consider an axis XX’ which is touching to two shells and passing through diameter of third shell. Moment of inertia of the system consisting of these three spherical shells about XX’ axis is
A. 11/5 m r^2
B. 3 m r^2
C. 16/5 m r^2
D. 4 m r^2
![]() Q. 13 Kepler’s third law states that square of period of revolution (T) of a planet around the Sun is proportional to third power of average distance r between Sun and planet i.e. T^2 = K r^3 here K is constant. If the masses of Sun and planet are M and m, respectively, then as per Newton’s law of gravitation, force of attraction between them is F = GMm/ r^2, here G is the gravitational constant. The relation between G and K is described as
Q. 13 Kepler’s third law states that square of period of revolution (T) of a planet around the Sun is proportional to third power of average distance r between Sun and planet i.e. T^2 = K r^3 here K is constant. If the masses of Sun and planet are M and m, respectively, then as per Newton’s law of gravitation, force of attraction between them is F = GMm/ r^2, here G is the gravitational constant. The relation between G and K is described as
A. GK = 4 π^2
B. GMK = 4 π^2
C. K = G
D. K = 1/G
![]() Q. 14 Two spherical bodies of mass M and 5 M and radii R and 2 R are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12 R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body before collision is
Q. 14 Two spherical bodies of mass M and 5 M and radii R and 2 R are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12 R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body before collision is
A. 2.5 R
B. 4.5 R
C. 7.5 R
D. 1.5 R
![]() Q. 15 On observing light from three different starts P, Q and R, it was found that intensity of violet colour is maximum in the spectrum of P, the intensity of green colour is maximum in the spectrum of R and the intensity of red colour is maximum in the spectrum of Q. If TP, TQ and TR are the respective absolute temperatures of P, Q and R, then it can be concluded from the above observation that
Q. 15 On observing light from three different starts P, Q and R, it was found that intensity of violet colour is maximum in the spectrum of P, the intensity of green colour is maximum in the spectrum of R and the intensity of red colour is maximum in the spectrum of Q. If TP, TQ and TR are the respective absolute temperatures of P, Q and R, then it can be concluded from the above observation that
A. TP > TQ > TR
B. TP > TR > TQ
C. TP < TR < TQ
D. TP < TQ < TR
![]() Q. 16 16. The approximate depth of an ocean is 2700 m. the compressibility of water is 45.4 x 10^(−11) Pa^(−1) and density of water is 10^3 kg/m^3. What fractional compression of water will be obtained at the bottom of the ocean?
Q. 16 16. The approximate depth of an ocean is 2700 m. the compressibility of water is 45.4 x 10^(−11) Pa^(−1) and density of water is 10^3 kg/m^3. What fractional compression of water will be obtained at the bottom of the ocean?
A. 0.8 x 10^(-2)
B. 1.0 x 10^(-2)
C. 1.2 x 10^(-2)
D. 1.4 x 10^(-2)
![]() Q. 17 The two ends of a metal rod maintained at temperatures 100 ⁰C and 110 ⁰C. The rate of heat flow in the rod is found to be 4.0 J/s. If the ends are maintained at temperatures 200 ⁰C and 210 ⁰C, the rate of heat flow will be
Q. 17 The two ends of a metal rod maintained at temperatures 100 ⁰C and 110 ⁰C. The rate of heat flow in the rod is found to be 4.0 J/s. If the ends are maintained at temperatures 200 ⁰C and 210 ⁰C, the rate of heat flow will be
A. 44.0 J/s
B. 16.8 J/s
C. 8.0 J/s
D. 4.0 J/s
![]() Q. 18 A wind with speed 40 m/s blows parallel to the roof of a house. The area of the roof is 250 m2. Assuming that the pressure inside the house is atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the wind on the roof and the direction of the force will be (P air = 1.2 kg/m3)
Q. 18 A wind with speed 40 m/s blows parallel to the roof of a house. The area of the roof is 250 m2. Assuming that the pressure inside the house is atmospheric pressure, the force exerted by the wind on the roof and the direction of the force will be (P air = 1.2 kg/m3)
A. 4.8 x 10^5 N, downwards
B. 4.8 x 10^5 N, upwards
C. 2.4 x 10^5 N, upwards
D. 2.4 x 10^5 N, downwards
![]() Q. 19 Figure below shows two paths that may be taken by a gas to go from a state A to a state C. In process AB, 400 J of heat is added to the system and in process BC, 100 J of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be
Q. 19 Figure below shows two paths that may be taken by a gas to go from a state A to a state C. In process AB, 400 J of heat is added to the system and in process BC, 100 J of heat is added to the system. The heat absorbed by the system in the process AC will be
A. 380 J
B. 500 J
C. 460 J
D. 300 J
![]() Q. 20 A Carnot engine having an efficiency of η=1/10 as heat engine is used as a refrigerator. If the work done on the system is 10 J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
Q. 20 A Carnot engine having an efficiency of η=1/10 as heat engine is used as a refrigerator. If the work done on the system is 10 J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
A. 100 J
B. 99 J
C. 90 J
D. 1 J
![]() Q. 21 One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from A to B along a path AB as shown in the figure,The change in internal energy of the gas during the transition is
Q. 21 One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from A to B along a path AB as shown in the figure,The change in internal energy of the gas during the transition is
A. 20 kJ
B. – 20 kJ
C. 20 J
D. -12 kJ
![]() Q. 22 The ratio of the specific heats Cp / Cy =γ in terms of degrees of freedom (n) is given by
Q. 22 The ratio of the specific heats Cp / Cy =γ in terms of degrees of freedom (n) is given by
A. 1 = 1/3
B. 1 + n/3
C. 1 + 2/n
D. 1+ n/2
![]() Q. 23 When two displacements represented by y1 = a sin (ωt) and y2 = b cos (ωt) are
Q. 23 When two displacements represented by y1 = a sin (ωt) and y2 = b cos (ωt) are
superimposed the motion is
A. Not a simple harmonic
B. Simple harmonic with amplitude a/b
C. Simple harmonic with amplitude √( a^2 + b^2 )
D. Simple harmonic with amplitude (a + b)/2
![]() Q. 24 A particle is executing SHM along a straight line. Its velocities at distances x1 and x2 from the mean position are V1 and V2, respectively. Its time period is
Q. 24 A particle is executing SHM along a straight line. Its velocities at distances x1 and x2 from the mean position are V1 and V2, respectively. Its time period is
A. 2π √( (x1^2 + x2^2)/(v1^2 + v2^2) )
B. 2π √( (x2^2 – x1^2)/(v1^2 – v2^2) )
C. 2π √( (v1^2 + v2^2)/(x1^2 + x2^2) )
D. 2π √( (v1^2 – v2^2)/(x1^2 – x2^2) )
![]() Q. 25 The fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe of length 20 cm is equal to the second overtone of an organ pipe open at both the ends. The length of organ pipe open at both ends is
Q. 25 The fundamental frequency of a closed organ pipe of length 20 cm is equal to the second overtone of an organ pipe open at both the ends. The length of organ pipe open at both ends is
A. 80 cm
B. 100 cm
C. 120 cm
D. 140 cm
![]() Q. 26 A parallel plate air capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a cell of emf V and then disconnected from it. A dielectric slab of dielectric constant K which can just fill the air gap of the capacitor is now inserted in it. Which of the following is incorrect?
Q. 26 A parallel plate air capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a cell of emf V and then disconnected from it. A dielectric slab of dielectric constant K which can just fill the air gap of the capacitor is now inserted in it. Which of the following is incorrect?
A. The potential difference between the plates decrease K times
B. The energy stored in the capacitor decreases K times
C. The change in energy stored is 1/2 ( C V^2)( 1/K – 1)
D. The charge on the capacitor is not conserved
![]() Q. 27 The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outward and is given by E = Ar. A charge contained in a sphere of radius ‘a’ centred at the origin of the field, will be given by
Q. 27 The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outward and is given by E = Ar. A charge contained in a sphere of radius ‘a’ centred at the origin of the field, will be given by
A. 4π ε0 Aa^2
B. ε0 Aa^2
C. 4π ε0 Aa^3
D. ε0 Aa^3
![]() Q. 28 A potentiometer wire has length 4 m and resistance 8 W. The resistance that must be connected in series with the wire and an accumulator of emf 2 V, so as to get a potential gradient 1 mV per cm on the wire is
Q. 28 A potentiometer wire has length 4 m and resistance 8 W. The resistance that must be connected in series with the wire and an accumulator of emf 2 V, so as to get a potential gradient 1 mV per cm on the wire is
A. 32 Ω
B. 40 Ω
C. 44 Ω
D. 48 Ω
![]() Q. 29 A, B and C are voltmeters of resistance R, 1.5R and 3R, respectively, as shown in the figure. When some potential difference is applied between X and Y, the voltmeter readings are VA, VB and VC, respectively, then
Q. 29 A, B and C are voltmeters of resistance R, 1.5R and 3R, respectively, as shown in the figure. When some potential difference is applied between X and Y, the voltmeter readings are VA, VB and VC, respectively, then
A. VA = VB = VC
B. VA ≠ VB = VC
C. VA = VB ≠ VC
D. VA ≠ VB ≠ VC
![]() Q. 30 Across a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross section a constant potential difference is applied. The quantity which remains constant along the conductor is
Q. 30 Across a metallic conductor of non-uniform cross section a constant potential difference is applied. The quantity which remains constant along the conductor is
A. current density
B. current
C. drift velocity
D. electric field
![]() Q. 31 A wire carrying current I has the shape as shown in adjoining figure. Linear parts of the wire are very long and parallel to X-axis, while semicircular portion of radius R is lying in Y–Z plane. Magnetic field at point O is
Q. 31 A wire carrying current I has the shape as shown in adjoining figure. Linear parts of the wire are very long and parallel to X-axis, while semicircular portion of radius R is lying in Y–Z plane. Magnetic field at point O is
A. B = (μ0 I / 4πR) ( πi + 2k )
B. B = – (μ0 I / 4πR) ( πi – 2k )
C. B = -(μ0 I / 4πR) ( πi + 2k )
D. B = (μ0 I / 4πR) ( πi – 2k )
![]() Q. 32 An electron moving in a circular orbit of radius r makes n rotations per second. The magnetic field produced at the centre has magnitude:
Q. 32 An electron moving in a circular orbit of radius r makes n rotations per second. The magnetic field produced at the centre has magnitude:
A. μ0 n e / 2πr
B. zero
C. μ0 n 2 e
D. μ0 r n e / 2r
![]() Q. 33 A conducting square frame of side ‘a’ and a long straight wire carrying current I are located in the same plane as shown in the figure. The frame moves to the right with a constant velocity ‘V’. The emf induced in the frame will be proportional to
Q. 33 A conducting square frame of side ‘a’ and a long straight wire carrying current I are located in the same plane as shown in the figure. The frame moves to the right with a constant velocity ‘V’. The emf induced in the frame will be proportional to
A. 1 / x^2
B. 1 / (2x – a)^2
C. 1 / (2x + a)^2
D. 1 / (2x + a)(2x – a)
![]() Q. 34 A resistance ‘R” draws power ‘P’ when connected to an AC source. if an inductance is now placed in series with the resistance, such that the impedance of the circuit becomes ‘Z’, the power drawn will be
Q. 34 A resistance ‘R” draws power ‘P’ when connected to an AC source. if an inductance is now placed in series with the resistance, such that the impedance of the circuit becomes ‘Z’, the power drawn will be
A. P ( R/Z )^2
B. P√(R/Z)
C. P ( R/Z )
D. P
![]() Q. 35 A resistance ‘R’ draws power ‘P’ when connected to an AC source. If an inductance is now placed in series with the resistance, such that the impedance of the circuit becomes ‘Z’, the power drawn will be
Q. 35 A resistance ‘R’ draws power ‘P’ when connected to an AC source. If an inductance is now placed in series with the resistance, such that the impedance of the circuit becomes ‘Z’, the power drawn will be
A. P ( R/Z)^2
B. P √(R/Z)
C. P ( R/Z)
D. E / C^2
![]() Q. 36 Two identical thin plano–convex glass lenses (refractive index 1.5) each having radius of curvature of 20 cm are placed with their convex surfaces in contact at the centre. The intervening space is filled with oil of refractive index 1.7. The focal length of the combination is
Q. 36 Two identical thin plano–convex glass lenses (refractive index 1.5) each having radius of curvature of 20 cm are placed with their convex surfaces in contact at the centre. The intervening space is filled with oil of refractive index 1.7. The focal length of the combination is
A. -20 cm
B. -25 cm
C. -50 cm
D. 50 cm
![]() Q. 37 For a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength ‘λ’, diffraction is produced by a single slit whose width ‘a’ is of the order of the wavelength of the light. If ‘D’ is the distance of the screen from the slit, the width of the central maxima will be
Q. 37 For a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength ‘λ’, diffraction is produced by a single slit whose width ‘a’ is of the order of the wavelength of the light. If ‘D’ is the distance of the screen from the slit, the width of the central maxima will be
A. 2Dλ/a
B. Dλ/a
C. Da/λ
D. 2Da/λ
![]() Q. 38 In a double slit experiment, the two slits are 1 mm apart and the screen is placed 1 m away. A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is used. What will be the width of each slit for obtaining ten maxima of double slit within the central maxima of single slit pattern?
Q. 38 In a double slit experiment, the two slits are 1 mm apart and the screen is placed 1 m away. A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is used. What will be the width of each slit for obtaining ten maxima of double slit within the central maxima of single slit pattern?
A. 0.2 mm
B. 0.1 mm
C. 0.5 mm
D. 0.02 mm
![]() Q. 39 The refracting angle of a prism is A, and refractive index of the material of the prism is cot (A/2). The angle of minimum deviation is
Q. 39 The refracting angle of a prism is A, and refractive index of the material of the prism is cot (A/2). The angle of minimum deviation is
A. 180° – 3A
B. 180° – 2A
C. 90° – A
D. 180°+ 2A
![]() Q. 40 A certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ. The stopping potential for photoelectric current for this light is 3V0. If the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is V0. The threshold wavelength for this surface for photoelectric effect is
Q. 40 A certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ. The stopping potential for photoelectric current for this light is 3V0. If the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 2λ, the stopping potential is V0. The threshold wavelength for this surface for photoelectric effect is
A. 6λ
B. 4λ
C. 4^λ
D. 6^λ
![]() Q. 41 Which of the following figures represent the variation of particle momentum and the associated de-Broglie wavelength?
Q. 41 Which of the following figures represent the variation of particle momentum and the associated de-Broglie wavelength?
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 42 Consider 3rd orbit of He+ (Helium), using non-relativistic approach, the speed of electron in this orbit will be [given K = 9 x 10^9 constant, Z = 2 and h(Planck’s constant) = 6.6 x 10^−34 Js]
Q. 42 Consider 3rd orbit of He+ (Helium), using non-relativistic approach, the speed of electron in this orbit will be [given K = 9 x 10^9 constant, Z = 2 and h(Planck’s constant) = 6.6 x 10^−34 Js]
A. 2.92 x 10^6 m/s
B. 1.46 x 10^6 m/s
C. 0.73 x 10^6 m/s
D. 3.0 x 10^6 m/s
![]() Q. 43 If radius of the 27/13 Al nucleus is taken to be R(Al) then the radius of 125/53 Te nucleus is nearly:
Q. 43 If radius of the 27/13 Al nucleus is taken to be R(Al) then the radius of 125/53 Te nucleus is nearly:
A. (53/13)^(1/3) R
B. 5/3 R
C. 3/5 R
D. 13/53 R
![]() Q. 44 If in a p–n junction, a square input signal of 10 V is applied, as shown
Q. 44 If in a p–n junction, a square input signal of 10 V is applied, as shown
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 45 Which logic gate is represented by the following combination of logic gates?
Q. 45 Which logic gate is represented by the following combination of logic gates?
A. OR
B. NAND
C. AND
D. NOR
![]() Q. 46 Which of the following species contains equal number of σ and π -bonds?
Q. 46 Which of the following species contains equal number of σ and π -bonds?
A. HCO₃⁻
B. XeO₄
C. CN₂
D. CH₂ CN₂
![]() Q. 47 The species Ar, K+ and Ca2+ contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase?
Q. 47 The species Ar, K+ and Ca2+ contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase?
A. Ar < K+ < Ca2+
B. Ca2+ < Ar <K+
C. Ca2+ < K+ < Ar
D. K+ < Ar < Ca2+
![]() Q. 48 The function of ‘’Sodium pump’’ is a biological process operating in each and every cell of all animals. Which of the following biologically important ions is also a constituent of this pump?
Q. 48 The function of ‘’Sodium pump’’ is a biological process operating in each and every cell of all animals. Which of the following biologically important ions is also a constituent of this pump?
A. Ca2+
B. Mg2+
C. K+
D. Fe2+
![]() Q. 49 ‘’Metals are usually not found as nitrates in their ores’’. Out of the following two (a and b) reasons which is/are true for the above observation?(a)Metal nitrates are highly unstable (b) Metal nitrates are highly soluble in water
Q. 49 ‘’Metals are usually not found as nitrates in their ores’’. Out of the following two (a and b) reasons which is/are true for the above observation?(a)Metal nitrates are highly unstable (b) Metal nitrates are highly soluble in water
A. a and b are true
B. a and b are false
C. a is false but b is true
D. a is true but b is false
![]() Q. 50 Solubility of the alkaline earth metal sulphates in water decreases in the sequence :
Q. 50 Solubility of the alkaline earth metal sulphates in water decreases in the sequence :
A. Mg > Ca > Sr > Ba
B. Ca > Sr > Ba > Mg
C. Sr > Ca > Mg > Ba
D. Ba > Mg > Sr > Ca
![]() Q. 51 Because of lanthanoid contraction, which of the following pairs of elements have nearly same atomic radii? (Numbers in the parenthesis are atomic numbers).
Q. 51 Because of lanthanoid contraction, which of the following pairs of elements have nearly same atomic radii? (Numbers in the parenthesis are atomic numbers).
A. Ti (22) and Zr (40)
B. Zr (40) and Nb (41)
C. Zr (40) and Hf (72)
D. Zr (40) and Ta (73)
![]() Q. 52 Which of the following processes does not involve oxidation of iron?
Q. 52 Which of the following processes does not involve oxidation of iron?
A. Rusting of iron sheets
B. Decolourisation of blue CuSO₄ solution by iron
C. Formation of FeCO₅ from Fe
D. Liberation of H² from steam by iron at high temperature
![]() Q. 53 Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
Q. 53 Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
A. CO₃²⁻ , SO₃²⁻
B. ClO₃²⁻ , CO₃²⁻
C. SO₃²⁻ , NO₃⁻
D. ClO₃⁻ , SO₃²⁻
![]() Q. 54 Which of the following options represents the correct bond order?
Q. 54 Which of the following options represents the correct bond order?
A. O₂⁻ >O₂ >O₂⁺
B. O₂⁻ <O₂ <O₂⁺
C. O₂⁻ >O₂ <O₂⁺
D. O₂- <O₂ >O₂⁺
![]() Q. 55 Nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide have some properties in common. Which property is shown by one of these compounds, but not by the other?
Q. 55 Nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide have some properties in common. Which property is shown by one of these compounds, but not by the other?
A. forms ‘acid – rain’
B. is a reducing agent
C. is soluble in water
D. is used as a food-preservative
![]() Q. 56 Maximum bond angle at nitrogen is present in which of the following
Q. 56 Maximum bond angle at nitrogen is present in which of the following
A. NO₂
B. NO₂⁻
C. NO₂⁺
D. NO₃⁻
![]() Q. 57 Magnetic moment 2.84 B.M. is given by: (At. nos. Ni = 28, Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27)
Q. 57 Magnetic moment 2.84 B.M. is given by: (At. nos. Ni = 28, Ti = 22, Cr = 24, Co = 27)
A. Ni₂⁺
B. Ti₃⁺
C. Cr₂⁺
D. Co₂⁺
![]() Q. 58 Cobalt (III) Chloride forms several octahedral complexes with ammonia. Which of the following will not give test for chloride ions with silver nitrate at 25°C?
Q. 58 Cobalt (III) Chloride forms several octahedral complexes with ammonia. Which of the following will not give test for chloride ions with silver nitrate at 25°C?
A. CoCl₃ . 3NH₃
B. CoCl₃ . 4NH₃
C. CoCl₃ . 5NH₃
D. CoCl₃ .6NH₃
![]() Q. 59 Which of these statements about [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ is true?
Q. 59 Which of these statements about [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ is true?
A. [[Co(CN)₆]³⁻ has no unpaired electrons and will be in a low-spin configuration
B. [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ has four unpaired electrons and will be in low-spin configuration
C. [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ has four unpaired electrons and will be in a high-spin configuration
D. [Co(CN)₆]³⁻ has no unpaired electrons and will e in a high-spin configuration
![]() Q. 60 The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope of which of the following graphs?
Q. 60 The activation energy of a reaction can be determined from the slope of which of the following graphs?
A. In K vs. T
B. InK/T vs.T
C. InKvs. 1/T
D. T/InK vs. 1/T
![]() Q. 61 Which one is not equal to zero for an ideal solution?
Q. 61 Which one is not equal to zero for an ideal solution?
A. ΔHmix
B. ΔSmix
C. ΔVmix
D. ΔP=Pobserved -PRaoult
![]() Q. 62 A mixture of gases contains H2 and O2 gases in the ratio of 1:4 (w/w). What is the molar ratio of the two gases in the mixture?
Q. 62 A mixture of gases contains H2 and O2 gases in the ratio of 1:4 (w/w). What is the molar ratio of the two gases in the mixture?
A. 1:4
B. 4:1
C. 16:1
D. 2:1
![]() Q. 63 A given metal crystallizes out with a cubic structure having edge length of 361 pm. If there are four metal atoms in one unit cell, what is the radius of one atom?
Q. 63 A given metal crystallizes out with a cubic structure having edge length of 361 pm. If there are four metal atoms in one unit cell, what is the radius of one atom?
A. 40 pm
B. 127 pm
C. 80 pm
D. 108 pm
![]() Q. 64 When initial concentration of a reactant is doubled in a reaction, its half – life period is not affected. The order of the reaction is :
Q. 64 When initial concentration of a reactant is doubled in a reaction, its half – life period is not affected. The order of the reaction is :
A. Zero
B. First
C. Second
D. More than zero but less than first
![]() Q. 65 If the value of an equilibrium constant for a particular reaction is 1.6 × 1012, then at equilibrium the system will contain
Q. 65 If the value of an equilibrium constant for a particular reaction is 1.6 × 1012, then at equilibrium the system will contain
A. All reactants
B. Mostly reactants
C. Mostly products
D. Similar amounts of reactants and products
![]() Q. 66 A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as :
Q. 66 A device that converts energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen and methane, directly into electrical energy is known as :
A. Fuel cell
B. Electrolytic cell
C. Dynamo
D. Ni–Cd cell
![]() Q. 67 The boiling point of 0.2 mol kg^−1 solution of X in water is greater than equimolal solution of Y in water. Which one of the following statements is true in this case?
Q. 67 The boiling point of 0.2 mol kg^−1 solution of X in water is greater than equimolal solution of Y in water. Which one of the following statements is true in this case?
A. X is undergoing dissociation in water
B. Molecular mass of X is greater than the molecular mass of Y
C. Molecular mass of X is less than the molecular mass of Y
D. Y is undergoing dissociation in water, while X undergoes no change
![]() Q. 68 Which one of the following electrolytes has the same value of van’t Hoff’s factor (i) as that of Al₂(SO₄)₃ (if all are 100% ionized)?
Q. 68 Which one of the following electrolytes has the same value of van’t Hoff’s factor (i) as that of Al₂(SO₄)₃ (if all are 100% ionized)?
A. K₂SO₄
B. K₃[Fe(CN)₆]
C. Al(NO₃)₃
D. K₄[Fe(CN)₆]
![]() Q. 69 The number of d-electrons in Fe2+ (Z = 26) is not equal to the number of electrons in which one of the following?
Q. 69 The number of d-electrons in Fe2+ (Z = 26) is not equal to the number of electrons in which one of the following?
A. s-electrons in Mg (Z = 12)
B. p-electrons in Cl (Z = 17)
C. d-electrons in Fe (Z = 26)
D. p-electrons in Ne (Z = 10)
![]() Q. 70 The correct bond order in the following species is:
Q. 70 The correct bond order in the following species is:
A. O²⁺₂ < O₂⁺ < O₂⁻
B. O²⁺₂ <O₂⁻ < O₂⁺
C. O₂⁺ < O₂⁻ < O²⁺₂
D. O₂⁻ < O₂⁺ < O²⁺₂
![]() Q. 71 The angular momentum of electron in ‘d’ orbital is equal to:
Q. 71 The angular momentum of electron in ‘d’ orbital is equal to:
A. √ 6 h
B. √2 h
C. 2 √3 h
D. 0 h
![]() Q. 72 The Ksp of Ag₂CrO₄, AgCl, AgBr and AgI are, respectively, 1.1 × 10⁻¹², 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰, 5.0 × 10⁻¹³, 8.3 × 10⁻¹⁷. Which one of the following salts will precipitate last if AgNO₃ solution is added to the solution containing equal moles of NaCl, NaBr, NaI and Na₂CrO₄
Q. 72 The Ksp of Ag₂CrO₄, AgCl, AgBr and AgI are, respectively, 1.1 × 10⁻¹², 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰, 5.0 × 10⁻¹³, 8.3 × 10⁻¹⁷. Which one of the following salts will precipitate last if AgNO₃ solution is added to the solution containing equal moles of NaCl, NaBr, NaI and Na₂CrO₄
A. AgI
B. AgCl
C. AgBr
D. AgCrO₄
![]() Q. 73 Which property of colloidal solution is independent of charge on the colloidal particles?
Q. 73 Which property of colloidal solution is independent of charge on the colloidal particles?
A. Coagulation
B. Electrophoresis
C. Electro-osmosis
D. Tyndall effect
![]() Q. 74 Which of the following statements is correct for a reversible process in a state of equilibrium?
Q. 74 Which of the following statements is correct for a reversible process in a state of equilibrium?
A. ΔG=-2.30RTlogK
B. ΔG=2.30RTlogK
C. ΔGo =-2.30RTlogK
D. ΔGo =2.30RTlogK
![]() Q. 75 Bithional is generally added to the soaps as an additive to function as a/an:
Q. 75 Bithional is generally added to the soaps as an additive to function as a/an:
A. Softener
B. Dryer
C. Buffering agent
D. Antiseptic
![]() Q. 76 The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces:
Q. 76 The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces:
A. P-Aminophenol
B. Azoxybenzene
C. Azobenzene
D. Aniline
![]() Q. 77 In Duma’s method for estimation of nitrogen 0.25 g of an organic compound gave 40 mL if nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 725 mm pressure. If the aqueous tension at 300 K is 25 mm, the percentage of nitrogen in the compound is:
Q. 77 In Duma’s method for estimation of nitrogen 0.25 g of an organic compound gave 40 mL if nitrogen collected at 300 K temperature and 725 mm pressure. If the aqueous tension at 300 K is 25 mm, the percentage of nitrogen in the compound is:
A. 17.36
B. 18.20
C. 16.76
D. 15.76
![]() Q. 78 In which of the following compounds, the C–Cl bond ionization shall give most stable carbonium ion?
Q. 78 In which of the following compounds, the C–Cl bond ionization shall give most stable carbonium ion?
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 79 The given reaction is
Q. 79 The given reaction is
A. Williamson Synthesis
B. Williamson continuous etherification process
C. Etard reaction
D. Gatterman–Koch reaction
![]() Q. 80 The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCH3 with HBr produces
Q. 80 The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCH3 with HBr produces
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 81 A single compound of the given structure is obtainable from ozonolysis of which of the following cyclic compounds
Q. 81 A single compound of the given structure is obtainable from ozonolysis of which of the following cyclic compounds
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 82 Treatment of cyclopentanone the following species?
Q. 82 Treatment of cyclopentanone the following species?
A. Cyclopentanonyl anion
B. Cyclopentadienyl cation
C. Cyclopentadienyl radical
D. Cyclopentanonyl biradical
![]() Q. 83 Consider the following compounds. The hyperconjugation occurs in?
Q. 83 Consider the following compounds. The hyperconjugation occurs in?
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I and III
![]() Q. 84 Which of the following is the most correct electron displacement of a nucleophilic reaction to take place
Q. 84 Which of the following is the most correct electron displacement of a nucleophilic reaction to take place
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 85 The enolic form of ethyl acetoacetate as below has:
Q. 85 The enolic form of ethyl acetoacetate as below has:
A. 18 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
B. 16 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bonds
C. 9 sigma bonds and 2 pi-bonds
D. 9 sigma bonds and 1 pi-bonds
![]() Q. 86 Given, Which of the given compounds can exhibit tautomerism?
Q. 86 Given, Which of the given compounds can exhibit tautomerism?
A. I and II
B. I and III
C. II and III
D. I, II and III
![]() Q. 87 The enthalpy of hydrogenation of these compounds will be in the order as:
Q. 87 The enthalpy of hydrogenation of these compounds will be in the order as:
A. I > II > III
B. III > II > I
C. II > III > I
D. II > I > III
![]() Q. 88 Biodegradable polymer which can be produced from glycine and aminocaproic acid is
Q. 88 Biodegradable polymer which can be produced from glycine and aminocaproic acid is
A. Nylon 2–nylon 6
B. PHBV
C. Buna-N
D. Nylon 6, 6
![]() Q. 89 The total number of π- bond electrons in the following structure is:
Q. 89 The total number of π- bond electrons in the following structure is:
A. 4
B. 8
C. 12
D. 16
![]() Q. 90 An organic compound ‘X’ having molecular formula C5H10O yields phenyl hydrazone and gives negative response to the iodoform test and Tollens’ test. It produces n-pentane on reduction. ‘X’ could be:
Q. 90 An organic compound ‘X’ having molecular formula C5H10O yields phenyl hydrazone and gives negative response to the iodoform test and Tollens’ test. It produces n-pentane on reduction. ‘X’ could be:
A. pentanal
B. 2-pentanone
C. 3-pentanone
D. n-amyl alcohol
![]() Q. 91 Which one of the following matches is correct?
Q. 91 Which one of the following matches is correct?
|
(1) |
Phytophthora |
Aseptate mycelium |
Basidiomycetes |
|
(2) |
Alternaria |
Sexual reproduction absent |
Deuteromycetes |
|
(3) |
Mucor |
Reproduction by conjugation |
Ascomycetes |
|
(4) |
Agaricus |
Parasitic fungus |
Basidiomycetes |
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 92 Read the following five statements (A to E) and select the option with all correct statements: (A) Mosses and Lichens are the first organisms to colonise a bare rock (B) Selaginella is a homosporous pteridophyte. (C) Coralloid roots in Cycas have VAM (D) Main plant body in bryophytes is gametophytic, whereas in pteridophytes is sporophytic (E) In gymnosperms, male and female gametophytes are present within sporangia located on sporophyte.
Q. 92 Read the following five statements (A to E) and select the option with all correct statements: (A) Mosses and Lichens are the first organisms to colonise a bare rock (B) Selaginella is a homosporous pteridophyte. (C) Coralloid roots in Cycas have VAM (D) Main plant body in bryophytes is gametophytic, whereas in pteridophytes is sporophytic (E) In gymnosperms, male and female gametophytes are present within sporangia located on sporophyte.
A. (A),(C) AND (D)
B. (B),(C) and (D)
C. (A),(D) and (E)
D. (B),(C) and (E)
![]() Q. 93 In which of the following gametophyte is not independent free living
Q. 93 In which of the following gametophyte is not independent free living
A. Funaria
B. Marchantia
C. Pteris
D. Pinus
![]() Q. 94 Which one of the following statements is wrong?
Q. 94 Which one of the following statements is wrong?
A. Algin and carrageenan are products of algae
B. Agar–agar is obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria
C. Chlorella and Spirulina are used as space food
D. Mannitol is stored food in Rhodophyceae
![]() Q. 95 The guts of cow and buffalo possess
Q. 95 The guts of cow and buffalo possess
A. Fucus spp.
B. Chlorella spp.
C. Methanogens
D. Cyanobacteria
![]() Q. 96 Male gametes are flagellated in
Q. 96 Male gametes are flagellated in
A. Polysiphonia
B. anabaena
C. Ectocarpus
D. Spirogyra
![]() Q. 97 Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are considered closed because
Q. 97 Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are considered closed because
A. A bundle sheath surrounds each bundle
B. Cambium is absent
C. There are no vessels with perforations
D. Xylem is surrounded all around by phloem
![]() Q. 98 The given figure is the floral image of
Q. 98 The given figure is the floral image of
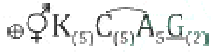
A. Allium
B. Sesbania
C. Petunia
D. Brassica
![]() Q. 99 A major characteristic of the monocot root is the presence of
Q. 99 A major characteristic of the monocot root is the presence of
A. Open vascular bundles
B. Scattered vascular bundles
C. Vasculature without cambium
D. Cambium sandwiched between phloem and xylem long the radius
![]() Q. 100 Keel is the characteristic feature of flower of
Q. 100 Keel is the characteristic feature of flower of
A. Tulip
B. Indigofera
C. Aloe
D. Tomato
![]() Q. 101 Perigynous flowers are found in
Q. 101 Perigynous flowers are found in
A. Guava
B. Cucumber
C. China rose
D. Rose
![]() Q. 102 Leaves become modified into spines in
Q. 102 Leaves become modified into spines in
A. Opuntia
B. Pea
C. Onion
D. Silk Cotton
![]() Q. 103 The structures that are formed by stacking of organised flattened membranous sacs in the chloroplasts are
Q. 103 The structures that are formed by stacking of organised flattened membranous sacs in the chloroplasts are
A. Cristae
B. Grana
C. Stroma lamellae
D. Stroma
![]() Q. 104 The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are
Q. 104 The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are
A. Metacentric
B. Acrocentric
C. Telocentric
D. Sub-metacentric
![]() Q. 105 Select the correct matching in the following pairs
Q. 105 Select the correct matching in the following pairs
A. Smooth R – Oxidation of phospholipids
B. Smooth ER – Synthesis of lipids
C. Rough ER – Synthesis of glycogen
D. Rough ER – Oxidation of fatty acids
![]() Q. 106 True nucleus is absent in
Q. 106 True nucleus is absent in
A. Anabaena
B. Mucor
C. Vaucheria
D. Volvox
![]() Q. 107 Which one of the following is not an inclusion body found in prokaryotes?
Q. 107 Which one of the following is not an inclusion body found in prokaryotes?
A. Phosphate granule
B. Cyanophycean granule
C. Glycogen granule
D. Polysome
![]() Q. 108 Transpiration and root pressure cause water to rise in plants by
Q. 108 Transpiration and root pressure cause water to rise in plants by
A. Pulling it upward
B. Pulling and pushing it, respectively
C. Pushing it upward
D. Pushing and pulling it, respectively
![]() Q. 109 Minerals known to be required in large amounts for plant growth include
Q. 109 Minerals known to be required in large amounts for plant growth include
A. Phosphorus, potassium, sulphur, calcium
B. Calcium, magnesium, manganese, copper
C. Potassium, phosphorus, selenium, boron
D. Magnesium, sulphur, iron, zinc
![]() Q. 110 What causes a green plant exposed to the light on only one side to bend toward the source of light as it grows?
Q. 110 What causes a green plant exposed to the light on only one side to bend toward the source of light as it grows?
A. Green plants need light to perform photosynthesis
B. Green plants seek because they are phototropic
C. Light stimulates plant cells on the lighted side to grow faster
D. Auxin accumulates on the shaded side, stimulating greater cell elongation there.
![]() Q. 111 In a ring girdled plant
Q. 111 In a ring girdled plant
A. The shoot dies first
B. The root dies first
C. The shoot and root die together
D. Neither root nor shoot will die
![]() Q. 112 Typical growth curve in plants is
Q. 112 Typical growth curve in plants is
A. Sigmoid
B. Linear
C. Stair–steps shaped
D. Parabolic
![]() Q. 113 Which one gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements?
Q. 113 Which one gives the most valid and recent explanation for stomatal movements?
A. Transpiration
B. Potassium influx and efflux
C. Starch hydrolysis
D. Guard cell photosynthesis
![]() Q. 114 The hilum is a scar on the
Q. 114 The hilum is a scar on the
A. Seed, where funicle was attached
B. Fruit, where it was attached to pedicel
C. Fruit, where style was present
D. Seed, where micropyle was present
![]() Q. 115 Which one of the following may require pollinators, but is genetically similar to autogamy?
Q. 115 Which one of the following may require pollinators, but is genetically similar to autogamy?
A. Geitonogamy
B. Xenogamy
C. Apogamy
D. Cleistogamy
![]() Q. 116 Which one of the following statement is not true?
Q. 116 Which one of the following statement is not true?
A. Pollen grains are rich in nutrients, and they used in the form of tablets and syrups
B. Pollen grains of some plants cause severe allergies and bronchial afflictions in some people
C. The flowers pollinated by flies and bats secrete four odour to attract them
D. Honey is made by bees by digesting pollen collected from flowers
![]() Q. 117 Transmission tissue is characteristics feature of
Q. 117 Transmission tissue is characteristics feature of
A. Hollow style
B. Solid style
C. Dry stigma
D. Wet stigma
![]() Q. 118 In ginger vegetative propagation occurs through
Q. 118 In ginger vegetative propagation occurs through
A. Rhizome
B. Offsets
C. Bulbils
D. Runners
![]() Q. 119 Which of the following are the important floral rewards to the animal pollinators?
Q. 119 Which of the following are the important floral rewards to the animal pollinators?
A. Colour and large size of flower
B. Nectar and pollen grains
C. Floral fragrance and calcium crystals
D. Protein pellicle and stigmatic exudates
![]() Q. 120 How many pairs of contrasting characters in pea plants were studied by Mendel in his experiments?
Q. 120 How many pairs of contrasting characters in pea plants were studied by Mendel in his experiments?
A. Five
B. Six
C. Seven
D. Eight
![]() Q. 121 Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism?
Q. 121 Which is the most common mechanism of genetic variation in the population of a sexually reproducing organism?
A. Transduction
B. Chromosomal aberrations
C. Genetic drift
D. Recombination
![]() Q. 122 A technique of micropropagation is
Q. 122 A technique of micropropagation is
A. Somatic hybridisation
B. Somatic embryogenesis
C. Protoplast fusion
D. Embryo rescue
![]() Q. 123 The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called
Q. 123 The movement of a gene from one linkage group to another is called
A. Inversion
B. Duplication
C. Translocation
D. Crossing over
![]() Q. 124 Multiple alleles are present
Q. 124 Multiple alleles are present
A. On different chromosomes
B. At different loci on the same chromosome
C. At the same locus of the chromosome
D. On non-sister chromatids
![]() Q. 125 Which body of the Government of India regulates GM research and safety of introducing GM organisms for public services?
Q. 125 Which body of the Government of India regulates GM research and safety of introducing GM organisms for public services?
A. Biosafety committee
B. Indian council of agricultural research
C. Genetic Engineering Approval committee
D. Research committee on Genetic Manipulation
![]() Q. 126 In BT cotton, the BT toxin present in plant tissue as pro-toxin is converted into active toxin due to
Q. 126 In BT cotton, the BT toxin present in plant tissue as pro-toxin is converted into active toxin due to
A. Alkaline pH of the insect gut
B. Acidic pH of the insect gut
C. Action of gut microorganisms
D. Presence of conversion factors in insect gut
![]() Q. 127 The crops engineered for glyphosate are resistant/tolerant to
Q. 127 The crops engineered for glyphosate are resistant/tolerant to
A. Fungi
B. Bacteria
C. Insects
D. Herbicides
![]() Q. 128 DNA is not present in
Q. 128 DNA is not present in
A. Chloroplast
B. Ribosomes
C. Nucleus
D. Mitochondria
![]() Q. 129 Which of the following enhances or induces fusion of protoplasts?
Q. 129 Which of the following enhances or induces fusion of protoplasts?
A. Sodium chloride and potassium chloride
B. Polyethylene glycol and sodium nitrate
C. IAA and kinetin
D. IAA and gibberellins
![]() Q. 130 The UN conference of Parties on climate change in the year 2011 was held in
Q. 130 The UN conference of Parties on climate change in the year 2011 was held in
A. Poland
B. South Africa
C. Peru
D. Qatar
![]() Q. 131 Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as
Q. 131 Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in a biotic community is known as
A. Divergence
B. Stratification
C. Zonation
D. Pyramid
![]() Q. 132 In which of the following both pairs have correct combination?
Q. 132 In which of the following both pairs have correct combination?
A. In situ conservation : National Park Ex situ conservation : Botanical Garden
B. In situ conservation : Cryopreservation Ex situ conservation : Wildlife sanctuary
C. In situ conservation : Seed Bank Ex situ conservation : National Park
D. In situ conservation : Tissue culture Ex situ conservation : Sacred groves
![]() Q. 133 Secondary succession takes place on/in
Q. 133 Secondary succession takes place on/in
A. Bare rock
B. Degraded forest
C. Newly created pond
D. Newly cooled lava
![]() Q. 134 The mass of living material at a trophic level at a particular time is called
Q. 134 The mass of living material at a trophic level at a particular time is called
A. Gross primary productivity
B. Standing state
C. Net primary productivity
D. Standing crop
![]() Q. 135 In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed
Q. 135 In an ecosystem the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is termed
A. Net primary productivity
B. Gross primary productivity
C. Secondary productivity
D. Net productivity
![]() Q. 136 Which of the following characteristics is mainly responsible for diversification of insects on land?
Q. 136 Which of the following characteristics is mainly responsible for diversification of insects on land?
A. Segmentation
B. Bilateral symmetry
C. Exoskeleton
D. Eyes
![]() Q. 137 Which of the following endoparasites of humans does show viviparity
Q. 137 Which of the following endoparasites of humans does show viviparity
A. Ancylostoma duodenale
B. Enterobius vermicularis
C. Trichinella spiralis
D. Ascaris lumbricoides
![]() Q. 138 Which of the following represents the correct combination without any exception?
Q. 138 Which of the following represents the correct combination without any exception?
A. (1)
B. (2)
C. (3)
D. (4)
![]() Q. 139 Which of the following animals is not viviparous?
Q. 139 Which of the following animals is not viviparous?
A. Flying fox (bat)
B. Elephant
C. Platypus
D. Whale
![]() Q. 140 Erythropoiesis starts in
Q. 140 Erythropoiesis starts in
A. Kidney
B. Liver
C. Spleen
D. Red bone marrow
![]() Q. 141 The terga, sterna and pleura of cockroach body are joined by
Q. 141 The terga, sterna and pleura of cockroach body are joined by
A. Cementing glue
B. Muscular tissue
C. Arthrodial membrane
D. Cartilage
![]() Q. 142 Nuclear envelope is a derivative of
Q. 142 Nuclear envelope is a derivative of
A. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
B. Membrane of Golgi complex
C. Microtubules
D. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
![]() Q. 143 Cytochromes are found in
Q. 143 Cytochromes are found in
A. Matrix of mitochondria
B. Outer wall of mitochondria
C. Cristae of mitochondria
D. Lysosomes
![]() Q. 144 Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
Q. 144 Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
A. A competitive inhibitor reacts reversibly with the enzyme to form an enzyme– inhibitor complex
B. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme
C. The competitive inhibitor does not affect the rate breakdown of the enzyme– substrate complex
D. The presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate
![]() Q. 145 Select the correct option for (a) (b) (c) (d)
Q. 145 Select the correct option for (a) (b) (c) (d)
A. (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
B. (ii) (iii) (v) (iv)
C. (i) (ii) (v) (iv)
D. (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
![]() Q. 146 A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle, as compared to gamete of the same species, has
Q. 146 A somatic cell that has just completed the S phase of its cell cycle, as compared to gamete of the same species, has
A. Twice the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA
B. Same number of chromosomes but twice the amount of DNA
C. Twice the number of chromosomes and four times the amount of DNA
D. Four times the number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA
![]() Q. 147 Which of the following statements is not correct?
Q. 147 Which of the following statements is not correct?
A. Brunner’s glands are present in the submucosa of stomach and secrete pepsinogen
B. Goblet cells are present in the mucosa of intestine and secrete mucus
C. Oxyntic cells are present in the mucosa of stomach and secrete HCl
D. Acini are present in the pancreas and secrete carboxypeptidase
![]() Q. 148 Gastric juice of infants contains
Q. 148 Gastric juice of infants contains
A. Maltase, pepsinogen, rennin
B. Nuclease, pepsinogen, lipase
C. Pepsinogen, lipase, rennin
D. Amylase, rennin, pepsinogen
![]() Q. 149 When you hold your breath, which of the following gas changes in blood would first lead to the urge to breathe?
Q. 149 When you hold your breath, which of the following gas changes in blood would first lead to the urge to breathe?
A. Falling O₂ concentration
B. Rising CO₂ concentration
C. Falling CO₂ concentration
D. Rising CO₂ and falling O₂ concentration
![]() Q. 150 Blood pressure in the mammalian aorta is maximum during
Q. 150 Blood pressure in the mammalian aorta is maximum during
A. Systole of the left atrium
B. Diastole of the right ventricle
C. Systole of the left ventricle
D. Diastole of the right atrium
![]() Q. 151 Which one of the following is correct?
Q. 151 Which one of the following is correct?
A. Plasma = Blood – Lymphocytes
B. Serum = Blood + Fibrinogen
C. Lymph = Plasma + RBC + WBC
D. Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
![]() Q. 152 Removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron will result in
Q. 152 Removal of proximal convoluted tubule from the nephron will result in
A. More diluted urine
B. More concentrated urine
C. No change in quality and quantity of urine
D. No urine formation
![]() Q. 153 Sliding filament theory can best explained as
Q. 153 Sliding filament theory can best explained as
A. When filaments slide past each other actin filaments shorten, while Myosin filament do not shorten
B. Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
C. Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
D. When myofilaments slide pass each other, Myosin filaments shorten, while Actin filaments do not shorte
![]() Q. 154 Glenoid cavity articulates
Q. 154 Glenoid cavity articulates
A. Clavicle with acromion
B. Scapula with acromion
C. Clavicle with scapula
D. Humerus with scapula
![]() Q. 155 Which of the following regions of the brain is incorrectly paired with its function?
Q. 155 Which of the following regions of the brain is incorrectly paired with its function?
A. Medulla oblongata – Homoeostatic control
B. Cerebellum – Language comprehension
C. Corpus callosum – Communication between the left and right cerebral cortices
D. Cerebrum – Calculation and contemplation
![]() Q. 156 A gymnast is able to balance his body upside down even in the total darkness because of
Q. 156 A gymnast is able to balance his body upside down even in the total darkness because of
A. Cochlea
B. Vestibular apparatus
C. Tectorial membrane
D. Organ of Corti
![]() Q. 157 A chemical signal that has both endocrine and neural roles is
Q. 157 A chemical signal that has both endocrine and neural roles is
A. Melatonin
B. Calcitonin
C. epinephrine
D. Cortisol
![]() Q. 158 Which of the following does not favour the formation of large quantities of dilute urine?
Q. 158 Which of the following does not favour the formation of large quantities of dilute urine?
A. Alcohol
B. Caffeine
C. Renin
D. Atrial-natriuretic factor
![]() Q. 159 Capacitation refers to changes in the
Q. 159 Capacitation refers to changes in the
A. Sperm before fertilisation
B. Ovum before fertilisation
C. Ovum after fertilisation
D. Sperm after fertilisation
![]() Q. 160 Which of these is not an important component of initiation of parturition in humans?
Q. 160 Which of these is not an important component of initiation of parturition in humans?
A. Increase in oestrogen and progesterone ratio
B. Synthesis of prostaglandins
C. Release of oxytocin
D. Release of prolactin
![]() Q. 161 Which of the following viruses is not transferred through semen of an infected male?
Q. 161 Which of the following viruses is not transferred through semen of an infected male?
A. Hepatitis B virus
B. Human immunodeficiency virus
C. Chikungunya virus
D. Ebola virus
![]() Q. 162 Which of the following cells during gametogenesis is normally diploid?
Q. 162 Which of the following cells during gametogenesis is normally diploid?
A. Primary polar body
B. Spermatid
C. Spermatogonia
D. Secondary polar body
![]() Q. 163 Hysterectomy is surgical removal of
Q. 163 Hysterectomy is surgical removal of
A. Uterus
B. Prostate gland
C. Vas deferens
D. Mammary glands
![]() Q. 164 Which of the following is not sexually transmitted disease?
Q. 164 Which of the following is not sexually transmitted disease?
A. Syphilis
B. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
C. Trichomoniasis
D. Encephalitis
![]() Q. 165 An abnormal human baby with ‘XXX’ sex chromosomes was born due to
Q. 165 An abnormal human baby with ‘XXX’ sex chromosomes was born due to
A. Formation of abnormal sperms in the father
B. Formation of abnormal ova in the mother
C. Fusion of two ova and one sperm
D. Fusion of two sperms and one ovum
![]() Q. 166 Alleles are
Q. 166 Alleles are
A. Different phenotype
B. True breeding homozygotes
C. Different molecular forms of a gene
D. Heterozygotes
![]() Q. 167 A man with blood group ‘A’ marries a woman with blood group ‘B’. What are all the possible blood groups of their offspring?
Q. 167 A man with blood group ‘A’ marries a woman with blood group ‘B’. What are all the possible blood groups of their offspring?
A. A and B only
B. A, B and AB only
C. A, B, AB and O
D. O only
![]() Q. 168 Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E. coli that involves the lac I gene product is
Q. 168 Gene regulation governing lactose operon of E. coli that involves the lac I gene product is
A. Positive and inducible because it can be induced by lactose
B. Negative and inducible because repressor protein prevents transcription
C. Negative and repressible because repressor protein prevents transcription
D. Feedback inhibition because excess of β – galactosidase can switch off transcription
![]() Q. 169 In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in the DNA are
Q. 169 In sea urchin DNA, which is double stranded, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. The percentages of the other three bases expected to be present in the DNA are
A. G 34%, A 24.5%, T 24.5%
B. G 17%, A 16.5%, T 32.5%
C. G 17%, A 33%, T 33%
D. G 8.5%, A 50%, T 24.5%
![]() Q. 170 Which of the following had the smallest brain capacity?
Q. 170 Which of the following had the smallest brain capacity?
A. Homo erectus
B. Homo sapiens
C. Homo neanderthalensis
D. Homo habilis
![]() Q. 171 A population will not exist in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium is
Q. 171 A population will not exist in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium is
A. Individuals mate selectively
B. There are no mutations
C. There is no migration
D. The population is large
![]() Q. 172 Match each disease with its correct type of vaccine for (a), (b), (c) and (d) are:
Q. 172 Match each disease with its correct type of vaccine for (a), (b), (c) and (d) are:
A. (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
B. (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
C. (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
D. (i) (ii) (iv) (iii)
![]() Q. 173 HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying
Q. 173 HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying
A. B-lymphocytes
B. Leukocytes
C. Helper T-lymphocytes
D. Thrombocytes
![]() Q. 174 To active form of Entamoeba histolytica feeds upon
Q. 174 To active form of Entamoeba histolytica feeds upon
A. Erythrocytes mucosa and submucosa of colon
B. Mucosa and submucosa of colon only
C. Food n intestine
D. Blood only
![]() Q. 175 High value of BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) indicates that
Q. 175 High value of BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) indicates that
A. Water is pure
B. Water is highly polluted
C. Water is less polluted
D. Consumption of organic matter in the water is higher by the microbes
![]() Q. 176 Most animals are tree dwellers in a
Q. 176 Most animals are tree dwellers in a
A. Coniferous forest
B. Thorn woodland
C. Temperate deciduous forest
D. Tropical rainforest
![]() Q. 177 The following graph depicts changes in two populations (A and B) of herbivores in a grassy field. A possible reason for these changes is that
Q. 177 The following graph depicts changes in two populations (A and B) of herbivores in a grassy field. A possible reason for these changes is that
A. Both plant populations in this habitat decreased
B. Population B compete more successfully for food than population A
C. Population A produced more offspring than population B
D. Population A consumed the members of population B
![]() Q. 178 Cryopreservation of gametes of threatened species in viable and fertile condition can be referred to as
Q. 178 Cryopreservation of gametes of threatened species in viable and fertile condition can be referred to as
A. In situ conservation of biodiversity
B. Advanced ex situ conservation of biodiversity
C. In situ conservation by sacred groves
D. In situ cryo-conservation of biodiversity
![]() Q. 179 Rachel Carson’s famous book ‘Silent spring’ is related to
Q. 179 Rachel Carson’s famous book ‘Silent spring’ is related to
A. Pesticide pollution
B. Noise pollution
C. Population explosion
D. Ecosystem management
![]() Q. 180 Which of the following is not one of the prime health risks associated with greater UV radiation through the atmosphere due to depletion of stratospheric ozone?
Q. 180 Which of the following is not one of the prime health risks associated with greater UV radiation through the atmosphere due to depletion of stratospheric ozone?
A. Increased skin cancer
B. Reduced immune system
C. Damage to eyes
D. Increased liver cancer
| Question | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Answer | C | B | B | B | C | C | A | A | C | D |
| Question | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| Answer | C | D | B | C | B | C | D | C | C | C |
| Question | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| Answer | B | C | C | B | C | D | C | A | A | B |
| Question | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| Answer | C | D | D | A | B | C | A | A | B | B |
| Question | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| Answer | B | B | B | D | C | B | C | C | C | A |
| Question | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| Answer | C | C | D | B | D | C | A | A | A | C |
| Question | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| Answer | B | B | B | B | C | A | A | D | B | D |
| Question | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| Answer | A | D | D | C | D | A | C | C | A | A |
| Question | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| Answer | A | A | C | C | A | D | B | A | B | C |
| Question | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 |
| Answer | B | C | D | D | C | C | B | C | C | B |
| Question | 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 |
| Answer | D | A | B | B | B | A | D | B | A | D |
| Question | 111 | 112 | 113 | 114 | 115 | 116 | 117 | 118 | 119 | 120 |
| Answer | B | A | B | A | A | D | B | A | B | D |
| Question | 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | 125 | 126 | 127 | 128 | 129 | 130 |
| Answer | D | B | C | C | C | A | D | B | B | B |
| Question | 131 | 132 | 133 | 134 | 135 | 136 | 137 | 138 | 139 | 140 |
| Answer | B | A | B | D | B | C | C | B | C | D |
| Question | 141 | 142 | 143 | 144 | 145 | 146 | 147 | 148 | 149 | 150 |
| Answer | C | D | C | D | B | C | A | C | B | C |
| Question | 151 | 152 | 153 | 154 | 155 | 156 | 157 | 158 | 159 | 160 |
| Answer | D | A | C | D | B | B | C | C | A | D |
| Question | 161 | 162 | 163 | 164 | 165 | 166 | 167 | 168 | 169 | 170 |
| Answer | C | C | A | D | B | C | C | B | C | D |
| Question | 171 | 172 | 173 | 174 | 175 | 176 | 177 | 178 | 179 | 180 |
| Answer | A | C | C | A | B | D | B | B | A | D |

